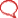
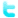Anatomy of the Female Reproductive system: Vagina, Cervix, Uterus, Fallopian tubes, Ovaries
sex Tags: Anatomy, Cervix, Fallopian, Female, Ovaries, Reproductive, System, tubes, Uterus, VaginaNo Comments »
►𝐉𝐨𝐢𝐧 𝐓𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐂𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐥 𝐓𝐨 𝐆𝐞𝐭 𝐀𝐜𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐓𝐨 𝐏𝐞𝐫𝐤𝐬 :- https://bit.ly/2RQHvTN
►𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐌𝐞𝐝𝐯𝐢𝐳𝐳 𝐚𝐩𝐩 𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐛𝐞𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐤 👇👇👇👇 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 👇👇👇👇
►𝐀𝐧𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐢𝐝 :- https://bit.ly/3ansFKq
📌𝐅𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐨𝐧 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦 :-
https://www.instagram.com/drgbhanuprakash
ANATOMY OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: Vagina, Cervix, Uterus, Fallopian tubes, Ovaries
The female reproductive system is a complicated but fascinating subject. It has the capability to function intimately with nearly every other body system for the purpose of reproduction.
The female reproductive organs can be subdivided into the internal and external genitalia (see the images below). The internal genitalia is those organs that are within the true pelvis. These include the vagina, uterus, cervix, uterine tubes (oviducts or fallopian tubes), and ovaries. The external genitalia lies outside the true pelvis. These include the perineum, mons pubis, clitoris, urethral (urinary) meatus, labia majora and minora, vestibule, greater vestibular (Bartholin) glands, Skene glands, and periurethral area.
Key Points
——————
A female’s internal reproductive organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix, and ovary.
External structures include the mons pubis, pudendal cleft, labia majora and minora, vulva, Bartholin’s gland, and the clitoris.
The female reproductive system contains two main parts: the uterus, which hosts the developing fetus, produces vaginal and uterine secretions, and passes the anatomically male sperm through to the fallopian tubes; and the ovaries, which produce the anatomically female egg cells.
Key Terms
——————
ovary: A female reproductive organ, often paired, that produces ova and in mammals secretes the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
oviduct: A duct through which an ovum passes from an ovary to the uterus or to the exterior (called fallopian tubes in humans).
vulva: The consists of the female external genital organs.
oogenesis: The formation and development of an ovum.
The human female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Uterus
———–
Hosts the developing fetus
Produces vaginal and uterine secretions
Passes the anatomically male sperm through to the fallopian tubes
Ovaries
Produce the anatomically female egg cells.
Produce and secrete estrogen and progesterone
These parts are internal; the vagina meets the external organs at the vulva, which includes the labia, clitoris, and urethra. The vagina is attached to the uterus through the cervix, while the uterus is attached to the ovaries via the fallopian tubes. At certain intervals, the ovaries release an ovum, which passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus.
If in this transit, it meets with sperm, the sperm penetrates and merges with the egg, fertilizing it. The fertilization usually occurs in the oviducts, but can happen in the uterus itself. The zygote then implants itself in the wall of the uterus, where it begins the process of embryogenesis and morphogenesis. When developed enough to survive outside the womb, the cervix dilates and contractions of the uterus propel the fetus through the birth canal (vagina).
The ova are larger than sperm and have formed by the time an anatomically female infant is born. Approximately every month, a process of oogenesis matures one ovum to be sent down the fallopian tube attached to its ovary in anticipation of fertilization. If not fertilized, this egg is flushed out of the system through menstruation.
An anatomically female’s internal reproductive organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix, and ovary.
The external components include the mons pubis, pudendal cleft, labia majora, labia minora, Bartholin’s glands, and clitoris.
#anatomyoffemalereproductivesystem #femalereproductivesystem #vagina #uterus #cervix #fallopiantubes #externalfemalegenitalia #femaleanatomy #femalegenitalia